What is Industrial Robotics and How Does it Transform Manufacturing?
Industrial robotics is rapidly reshaping the landscape of manufacturing. These advanced systems are designed to automate tasks conventionally performed by humans. From welding to packaging, industrial robotics enhances efficiency and precision. Companies are increasingly adopting robots to keep pace with market demands.
The integration of industrial robotics brings significant benefits. It reduces labor costs and minimizes human error. However, the initial investment can be daunting for smaller businesses. Not every factory is ready for this transformation. Additionally, there are concerns about job displacement as machines take over certain roles.
Despite these challenges, industrial robotics offers a path to innovation. With the right approach, manufacturers can optimize their operations. The key lies in balancing technology and human skills. Embracing this change requires careful planning and the courage to adapt.

What is Industrial Robotics?
Industrial robotics is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape. It involves the use of automated machines to perform repetitive tasks. These robots are designed to increase efficiency and consistency in production lines. According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global industrial robot population reached 3 million units in 2020. This marks a 12% annual growth rate, reflecting a significant shift in operational practices.
The technology enhances precision and reduces waste. For instance, robots can execute assembly tasks with an accuracy of +/- 0.01 mm. However, the integration of robotics isn't without challenges. Many workers face job displacement concerns, as tasks once performed by humans become automated. The transition to an automated system requires careful planning and investment in workforce retraining. The World Economic Forum reports that 85 million jobs may be displaced due to automation by 2025, highlighting a critical issue.
Adopting industrial robotics invites a deeper reflection on the future of work. Companies must ensure that advancements do not leave employees behind. It is vital to create a balance between increased production and job security. Though the benefits of industrial robotics are clear, the conversation around ethical implementation is just beginning. As this technology evolves, so must our approach to its integration in the workforce.
Key Components of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots play a vital role in modern manufacturing. These machines enhance productivity and precision. Key components of industrial robots include the manipulator, the end effector, and the control system. Each element is crucial for the robot's function. The manipulator is the robot's arm, which performs a variety of tasks. It can move in multiple directions to access various areas.
The end effector is the tool attached to the manipulator. This might be a gripper, a welding torch, or a paint sprayer. The choice of end effector significantly affects the robot's task capabilities. Inappropriate choices can lead to inefficiencies or damaged products. The control system oversees the robot’s operations. It interprets programming and directs movements. If the programming is flawed, the robot may work incorrectly.
These components work together harmoniously. However, not all robots are perfect. Sometimes, they misread signals or miscalculate motions. This can lead to accidents or costly errors. Manufacturers must regularly assess their robotic systems. Reflecting on performance is essential for improvements. In a rapidly changing industry, adaptability is key.
Industrial Robotics Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
This chart illustrates the efficiency metrics of manufacturing processes before and after the implementation of industrial robotics across key components. As shown, significant improvements are observed in production speed and reduction in error rates, showcasing the transformative power of industrial robots in manufacturing environments.
Applications of Industrial Robotics in Manufacturing
Industrial robotics has become essential in modern manufacturing. These machines perform tasks with high precision and speed, often beyond human capabilities. They work in various sectors, from automotive to electronics. For instance, robots assemble components, weld parts together, and even handle heavy materials. Their ability to repeat tasks tirelessly boosts production rates significantly.
Despite their advantages, challenges remain. Integrating robotics can disrupt traditional workflows. Workers must adapt to new roles, which may lead to resistance. Moreover, proper maintenance is crucial. A malfunctioning robot affects the entire assembly line. Some companies face hurdles in training staff to operate and troubleshoot robotic systems. Balancing human and robotic collaboration is key to maximizing benefits while minimizing disruptions.
What is Industrial Robotics and How Does it Transform Manufacturing? - Applications of Industrial Robotics in Manufacturing
| Application | Description | Benefits | Industry Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding | Robotic welding machines perform precise and repetitive welding operations on metal parts. | Increased speed, improved weld quality, and reduced human error. | Automotive, Aerospace |
| Assembly | Robots are utilized for assembling components in a fast and efficient manner. | Faster assembly times and the ability to work continuously without fatigue. | Electronics, Consumer Goods |
| Packaging | Industrial robots are employed to pack products into boxes or pallets. | Enhanced efficiency and consistency in packaging operations. | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals |
| Material Handling | Robots are used for transporting materials between different locations within a manufacturing facility. | Increased workplace safety and reduced labor costs. | Warehouse, Logistics |
| Inspection | Robotic systems equipped with sensors perform quality control inspections on products. | Higher accuracy in defect detection and enhanced product quality. | Manufacturing, Electronics |
Benefits of Implementing Robotics in Production Processes
Implementing robotics in production processes brings numerous benefits. Automation speeds up manufacturing. Robots can work tirelessly, leading to higher efficiency. They are precise, reducing errors in assembly lines. This leads to better product quality. With automation, companies can scale production easily.
Tips: Always assess the specific needs of your production. Not every task is suitable for robots. Some processes still require human oversight. Integrating robotics can be costly at first. Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before proceeding.
Robots can also take on dangerous tasks. This enhances workplace safety. Workers can focus on more complex, creative tasks. However, a shift to robotics may cause resistance among staff. Addressing these concerns is essential for a smooth transition. Continuous training and communication are vital.
Future Trends Shaping Industrial Robotics and Manufacturing
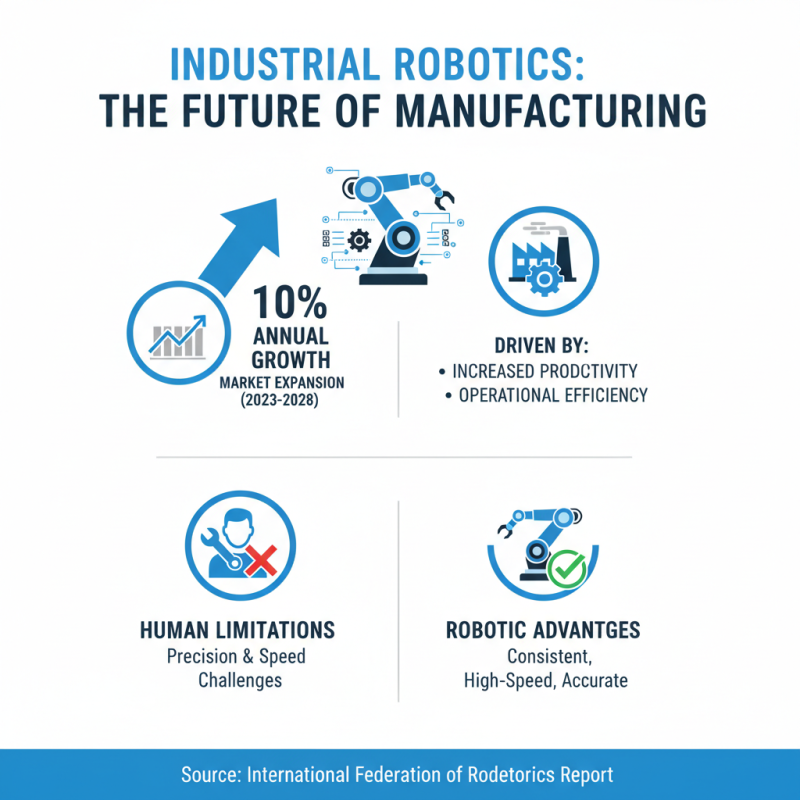
Industrial robotics is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advances and changing market demands. According to a recent report by the International Federation of Robotics, the market for industrial robots is expected to grow by nearly 10% annually over the next five years. This growth is primarily fueled by the need for increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Factories are now integrating robots to perform tasks that require precision and speed, which humans may struggle to accomplish consistently.
However, the rise of automation raises questions about workforce displacement. Many manufacturing jobs may vanish as robots take over repetitive tasks. A study by McKinsey Global Institute suggests that by 2030, up to 800 million jobs could be at risk due to automation. This presents a challenge for industries to reskill their workforce. Finding the balance between technology and human labor remains a complex issue.
Future trends also point toward the incorporation of artificial intelligence in robotics. Smart robots can learn from their environments, adapting to changes in real-time. This increases operational flexibility but requires careful implementation and oversight. If not managed properly, reliance on AI could lead to over-dependence and a lack of human oversight. Robotics is transforming manufacturing, but the journey is fraught with both opportunities and challenges.
Related Posts
-

The Rapid Growth of Industrial Robotics Revolutionizing Manufacturing with 80 Percent Productivity Increase
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: How Industrial Robotics Are Shaping the Future of Automation
-

Top 10 Industrial Robotics Innovations Revolutionizing Manufacturing
-

How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Robots for Your Production Needs
-

Why Choose a Pick and Place Robot? Boost Efficiency with 70% Increased Productivity
-

Top 7 Manufacturing Robots Revolutionizing the Industry in 2023


