Top Features of 6 Axis Robot Arm in Modern Automation Technology?
The 6 axis robot arm has transformed modern automation technology significantly. This advanced robotic system enhances productivity across various industries. Its versatility is a game changer for manufacturing, assembly, and packaging tasks.
These robotic arms mimic human arm movements. They feature six joints, allowing for a wide range of motion. This flexibility enables them to complete intricate tasks with precision. Industries benefit from increased efficiency, reduced errors, and lower labor costs. However, relying solely on automation raises questions about job displacement and skill shifts.
While the 6 axis robot arm offers many advantages, challenges remain. Some tasks still require human touch. Balancing automation with human input is key to a successful future in automation. The potential of this technology is immense, yet careful implementation is necessary to address these concerns.
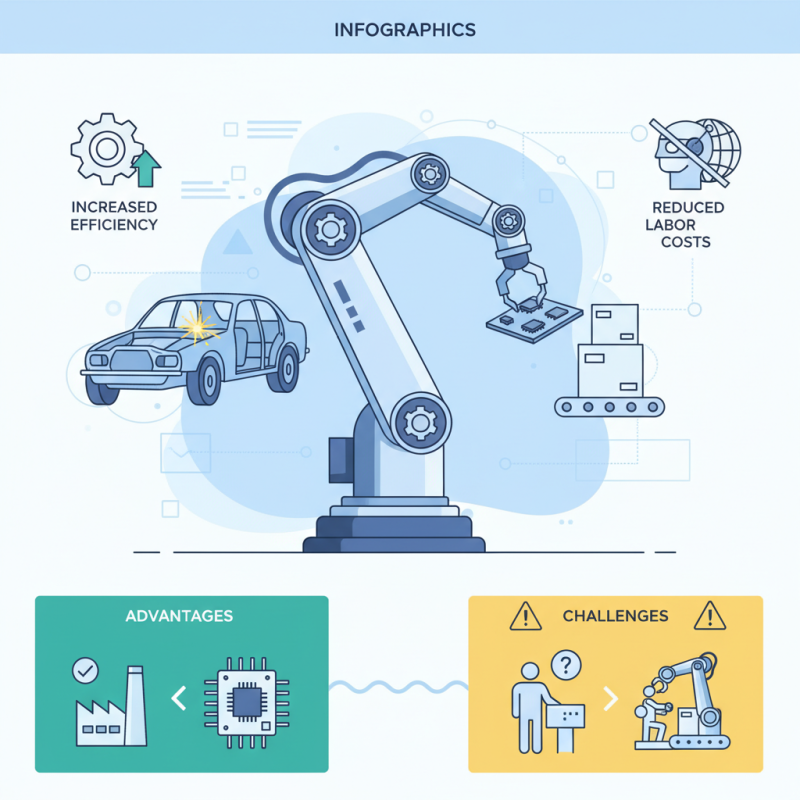
Key Components of a 6 Axis Robot Arm in Automation
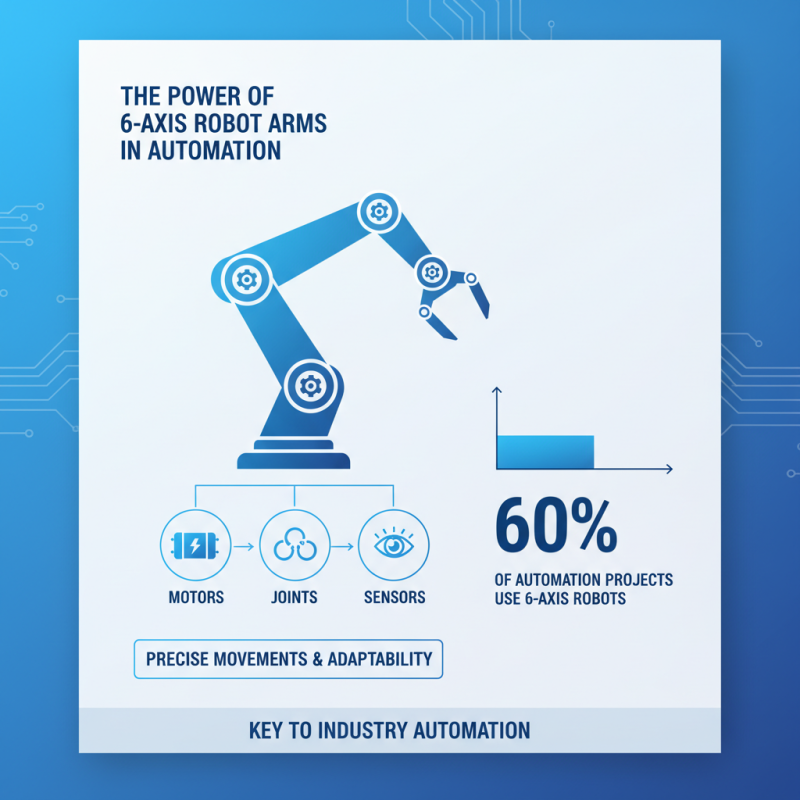
The six-axis robot arm plays a crucial role in automation technology. It consists of multiple key components that enhance its functionality. At the core, the robotic arm features motors, joints, and sensors. These work together to provide precise movements and adaptability. Reports indicate that nearly 60% of automation projects utilize six-axis robots, highlighting their importance in the industry.
The servo motors drive the arm's joints, allowing for smooth movement. High precision is achieved thanks to advanced encoders. Meanwhile, the control systems integrate with sensors to ensure accurate positioning. This combination leads to enhanced productivity in manufacturing. Data from industry experts shows that such robots can improve production rates by up to 30%.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain. The calibration of six-axis arms requires time and expertise. Additionally, maintenance can be complex, leading to potential downtimes. Industry surveys show that many users cite these issues as barriers to full implementation. Reflecting on these shortcomings is essential for improving the technology further.
Mechanisms of Movement: Understanding the 6 Degrees of Freedom
The 6 axis robot arm features an impressive capability known as the 6 degrees of freedom. This allows it to move freely in three-dimensional space. Each axis provides one degree of freedom, enabling the arm to rotate and pivot in multiple directions. This flexibility opens up possibilities for various applications in automation.
Understanding the mechanisms behind each joint reveals how the robot arm achieves this movement. The first three axes generally control the arm's base, allowing for rotation around its vertical axis. The next two axes are responsible for raising and lowering the arm. The sixth axis typically handles the end effector, allowing intricate movements. This design must be precise. Any misalignment can impact performance.
However, programming these movements remains a challenge. Unexpected obstacles may arise during tasks. The complexity of coordinating each joint can lead to errors. Additionally, fine-tuning the robot requires continuous adjustments for optimal operation. These reflections on the limitations of such technology highlight areas for improvement in future designs.
Top Features of 6 Axis Robot Arm in Modern Automation Technology
This chart illustrates the importance of the six degrees of freedom (DoF) in modern 6-axis robot arms, emphasizing how each degree contributes to enhanced movement capabilities in automation technology.
Applications of 6 Axis Robot Arms in Various Industries
6 Axis Robot Arms are transforming various industries. Their versatility makes them ideal for tasks like welding, painting, and assembly. In the automotive sector, these robots handle complex tasks with precision. They can grasp, move, and position heavy parts effortlessly. This capability increases production speed.
In electronics manufacturing, 6 Axis Robots perform delicate operations. They assemble tiny components with high accuracy. These tasks require careful manipulation, and robots excel in this area. However, sometimes they struggle with intricate designs. Adjustments may be necessary to improve their performance.
Food processing also benefits from this technology. Robots package products quickly and securely. They can operate in environments with strict hygiene standards. Yet, the setup can be challenging. Ensuring proper sanitization is critical. Monitoring systems may need enhancements for better efficiency.
Top Features of 6 Axis Robot Arm in Modern Automation Technology
| Feature | Description | Applications | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Capable of performing a wide range of tasks with varying degrees of complexity. | Assembly, welding, painting | Manufacturing |
| Precision | High accuracy in tasks, reducing human error significantly. | Precision machining, electronics assembly | Electronics |
| Safety | Equipped with advanced safety features to protect human workers. | Collaborative applications | Logistics |
| Speed | Fast operational speeds enabling high throughput. | Packaging, sorting | Food & Beverage |
| Compact Design | Space-saving design suitable for small workspaces. | Assembly line automation | Consumer Goods |
Advantages of Using 6 Axis Robot Arms in Manufacturing Processes
The use of 6-axis robot arms in manufacturing processes offers significant advantages. Their flexibility allows them to perform complex tasks that were once impossible for traditional robots. These arms can navigate around obstacles and reach difficult angles. This adaptability is crucial in efficient production lines where space is limited.
In addition, 6-axis robots improve precision in tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly. They can execute repetitive tasks with high accuracy, reducing human error. However, implementing these advanced systems requires careful planning and training. Many operators may struggle with programming these robots effectively. This can lead to suboptimal use of resources and potential downtimes.
Additionally, 6-axis robots can enhance productivity significantly, but they come with challenges. Maintenance can be demanding, requiring skilled technicians. Despite their advantages, companies must evaluate the cost-benefit ratio. High initial investments may cause hesitation for some. Ultimately, a well-implemented 6-axis robot arm can transform manufacturing processes, but it does come with its hurdles.
Future Trends in 6 Axis Robotics and Automation Technology
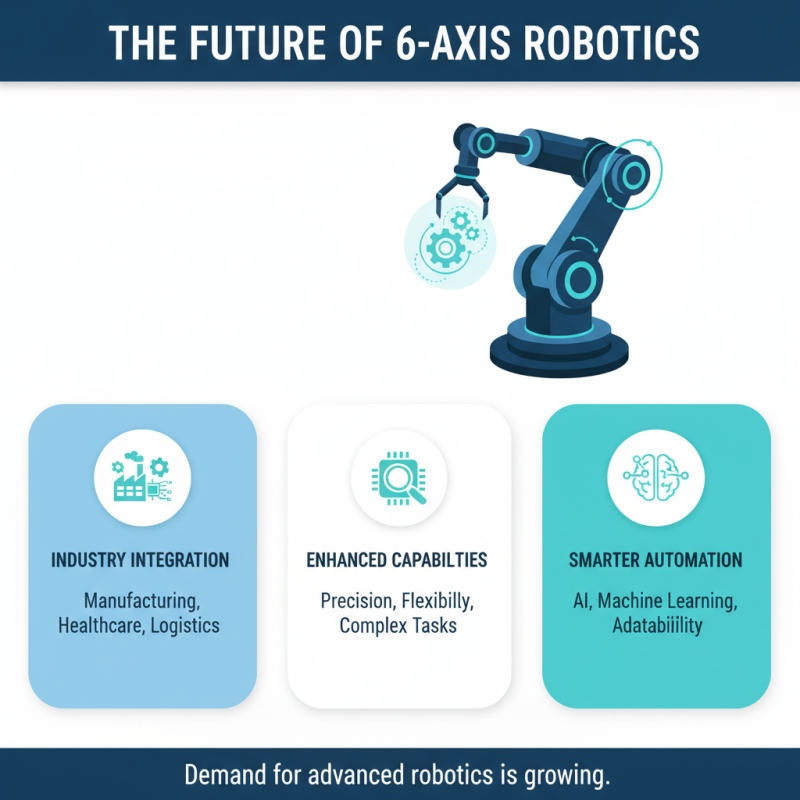
The future of 6-axis robotics looks promising. These robots are becoming more integrated into various industries. They provide enhanced precision and flexibility. This versatility allows them to perform complex tasks effortlessly. As industries evolve, the demand for smarter automation technology grows.
Emerging trends focus on artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies enable robots to adapt to new environments. They can learn from their experiences. This makes them more efficient over time. However, the integration process can be challenging. There’s a need for better programming interfaces and user-friendly designs.
As automation advances, collaboration between humans and robots is crucial. This synergy could enhance workplace productivity. Yet, there are risks of job displacement. Balancing efficiency with workforce stability is a significant concern. Reflecting on the ethical aspects of automation is essential. Future developments must address these complexities.
Related Posts
-

How to Use a Robot Arm for Automation in 2026?
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Industrial Robot Arms in Modern Manufacturing
-

What is Industrial Robotics and How Does it Transform Manufacturing?
-

What is Robotic Arm Design and Its Applications?
-

Revolutionizing Automation: How Cartesian Robots Shape the Future of Precision Engineering
-

2026 Best XYZ Gantry Systems for Precision Engineering?


