What Are the Top Manufacturing Robots Transforming Industries Today?
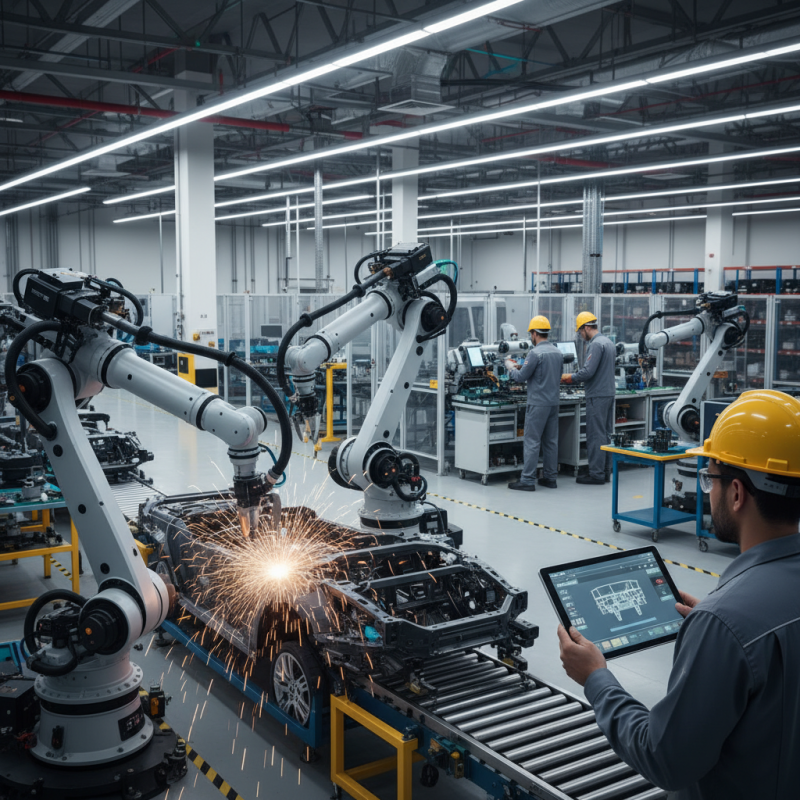
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, robots are reshaping the landscape. Industry expert Dr. Emma Chen highlights, “Manufacturing robots are not just tools; they are integral to future production.” This shift is vital for companies trying to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Manufacturing robots now perform complex tasks that were once dependent on human labor. They improve precision and speed in industries like automotive and electronics. However, the rush towards automation raises questions about job security. Many fear that robots may replace skilled workers instead of enhancing their roles.
The deployment of manufacturing robots comes with challenges. Not every company can afford the latest technology. Additionally, integrating robots into existing workflows can be a daunting task. As we embrace this robotic revolution, a careful balance must be struck between innovation and the workforce's stability. The future of manufacturing depends on this harmony.

The Rise of Collaborative Robots in Manufacturing Processes
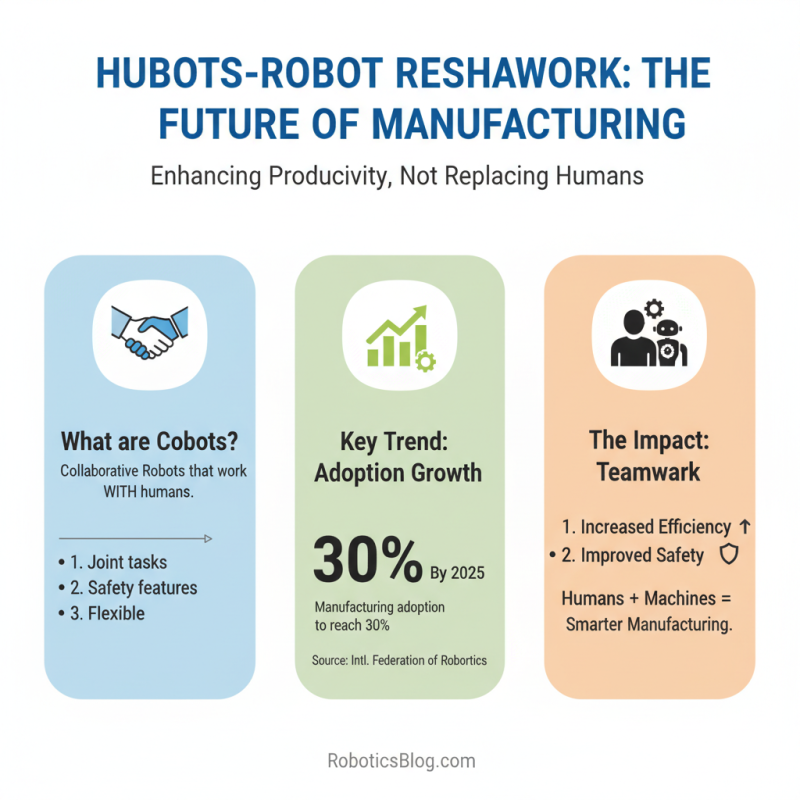
The rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, is reshaping manufacturing. These robots work alongside humans, enhancing productivity without replacing them. According to a recent report from the International Federation of Robotics, the adoption of cobots in manufacturing will reach 30% by 2025. This shift highlights a growing trend towards teamwork between humans and machines.
Cobots are designed for safety and ease of use. They require minimal training, which allows teams to adapt quickly. In many factories, operators see an increase in efficiency. Still, limitations exist. Not all tasks are suitable for cobots. Certain complex processes need skilled human intervention. Understanding when to use cobots is critical for manufacturers.
Data shows that 58% of companies reported productivity improvements after integrating cobots. However, challenges like resistance from workers are common. It’s essential to address these concerns through education. The goal is to create a collaborative environment where both humans and robots thrive together. Balancing technology with human skills remains an ongoing discussion in the industry.
Impact of Industrial Robots on Supply Chain Efficiency and Productivity
Industrial robots are revolutionizing supply chains and enhancing productivity across various sectors. According to a report by McKinsey, the use of robots can increase efficiency by over 30%. This capability stems from their ability to execute repetitive tasks without fatigue. However, this transformation is not without challenges.
Implementing robots requires significant investment and training. Reports indicate that around 30% of companies struggle with integration. Employees may resist automation, fearing job displacement. Balancing human and robotic collaboration is crucial for success. Many firms are exploring hybrid models to optimize workflows while retaining human oversight.
Moreover, increased reliance on robotic systems can lead to vulnerabilities. A malfunction can disrupt production, causing delays. According to a study by Deloitte, 70% of companies experienced downtime due to robot failure. This highlights the need for robust maintenance programs. Organizations must learn to navigate these complexities to fully harness the benefits of industrial robots.
Key Industries Adopting Automation: Automotive, Electronics, and Beyond
The adoption of automation in key industries is reshaping the landscape of manufacturing. In the automotive sector, for example, studies indicate that over 75% of manufacturers are integrating robotic systems into their production lines. Robots enhance efficiency and precision, leading to higher output rates. Yet, as companies shift to automation, challenges arise in workforce training. Many workers need to upskill to keep pace with new technologies.
Electronics manufacturing also heavily relies on automation. Reports show that automated systems can increase production speed by up to 30%. This has led to significant cost reductions. However, there’s a downside. With a high reliance on robots, some companies struggle to adapt to rapid technological changes. Flexibility and resilience in workforce development become crucial to address skill gaps.
Beyond automotive and electronics, other sectors like food processing are embracing robots. Automation in food packaging can reduce labor costs by 20%. But this shift may lead to concerns about job displacement. Companies must navigate this delicate balance. Investing in employee retraining programs is essential. Failing to do so may result in a workforce that is ill-equipped for the future.
Top Manufacturing Robots Transforming Industries
Statistics on Job Displacement vs. Job Creation by Manufacturing Robots
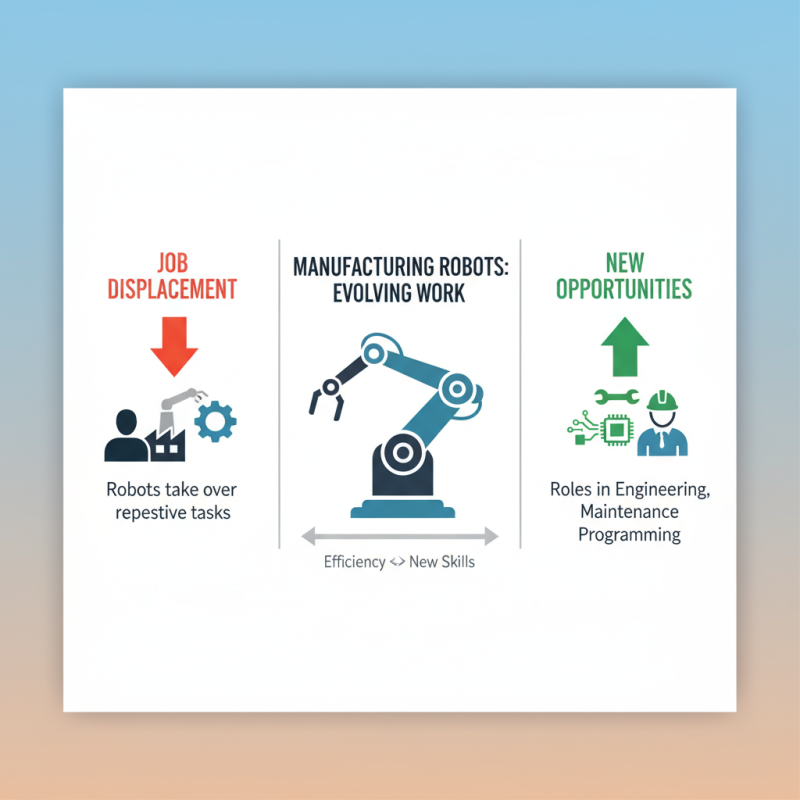
The rise of manufacturing robots is changing the workforce landscape dramatically. On one hand, their efficiency leads to job displacement. In many sectors, robots are taking over repetitive tasks. This raises concerns for workers in those roles. However, there is also a positive side. New jobs are created in engineering, maintenance, and programming. These roles require different skills compared to traditional positions.
Statistics show a mixed impact. Many fear the loss of jobs to robots. Yet, studies indicate that automation can create more jobs than it displaces. For instance, each robot may eliminate a few positions but generate demand for skilled workers. This shift emphasizes the need for training and upskilling in the workforce.
**Tip:** Embrace lifelong learning. Stay current with tech trends. Workers can adapt to new roles in this evolving environment.
It’s important to openly discuss the fears related to job loss. Companies should recognize employee concerns and facilitate transitions. Open communication can ease anxieties and promote a cooperative atmosphere. Balancing automation with human employment will be crucial for the future of industries.
**Tip:** Advocate for educational programs. Partner with organizations to provide resources for skill development. This proactive approach benefits both employers and employees.
Future Trends: AI Integration in Manufacturing Robots and Industry 4.0
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in manufacturing robots is increasingly shaping the future of Industry 4.0. According to a report by PwC, over 50% of companies are investing in AI initiatives for their manufacturing processes. AI technologies are helping robots become more adaptive and efficient. These robots can learn from their environment and make real-time decisions. This ability enhances productivity but raises questions about job displacement in traditional roles.
Automation is set to grow, with research from McKinsey indicating that 45% of tasks can be automated using existing technology. Yet, challenges remain. Businesses must balance automation with human oversight. AI isn't infallible; errors can occur, impacting quality. According to Deloitte, 67% of manufacturers cite integration difficulties when deploying AI systems. This illustrates that while the technology is promising, it requires careful planning and execution.
As industries advance, the role of humans is evolving. Workers now focus on supervising automated systems rather than performing repetitive tasks. There’s a gap in skills needed to work alongside these advanced robots. Continuous training is critical. The need for workforce reskilling is pressing, with 70% of executives reporting skills shortages. Adapting to these changes is essential for sustainable growth and innovation in manufacturing.
What Are the Top Manufacturing Robots Transforming Industries Today?
| Robot Type | Application | Integration Level | Industry Impact | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Articulated Robots | Assembly, Welding | High | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs | Greater AI function, collaborative capabilities |
| SCARA Robots | Pick and Place | Medium | Higher throughput, precision tasks | Integration with IoT for real-time processing |
| Delta Robots | Packaging, Sorting | High | Fast handling of delicate items | Enhanced speed through AI algorithms |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Assembly, Quality Inspection | Medium | Improved safety, enhanced human-robot collaboration | Integration with advanced sensors for better interaction |
| Mobile Robots | Material Handling | High | Streamlined logistics, reduced transport time | AI for autonomous navigation and decision making |
Related Posts
-

The Rapid Growth of Industrial Robotics Revolutionizing Manufacturing with 80 Percent Productivity Increase
-

Exploring the Future of Manufacturing Robots in Smart Factories
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: How Pick and Place Robots Optimize Efficiency by 30% in Production Lines
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: How Industrial Robotics Are Shaping the Future of Automation
-
Exploring the Future of Manufacturing: The Rise of Cartesian Robots in Automation
-

Revolutionizing Automation: How Cartesian Robots Shape the Future of Precision Engineering


