Top Types of Cartesian Robots in Automation and Their Applications?
The demand for automation in industries is rapidly growing. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global industrial robotics market is projected to reach $75 billion by 2025. Among these innovations, the cartesian robot stands out due to its versatility and precision. These robots are designed for simple linear movements, which makes them ideal for pick-and-place tasks, assembly, and packaging.
Cartesian robots utilize a three-axis system to achieve exceptional accuracy. The simplicity of their structure allows for easy integration into existing production lines. A study by ResearchAndMarkets noted that over 30% of robotic implementations in factories involve cartesian robots, highlighting their significance in automation. However, while they are efficient, organizations must be aware of their limitations. These robots may not adapt as easily to complex tasks compared to other robotic types.
Industries such as electronics, food packaging, and pharmaceuticals extensively utilize cartesian robots. Their ability to maintain consistent performance increases productivity and reduces labor costs. Yet, companies must critically evaluate their specific needs and explore alternative options, if necessary. Balancing automation strategy with real-world applications is crucial for achieving optimal results.
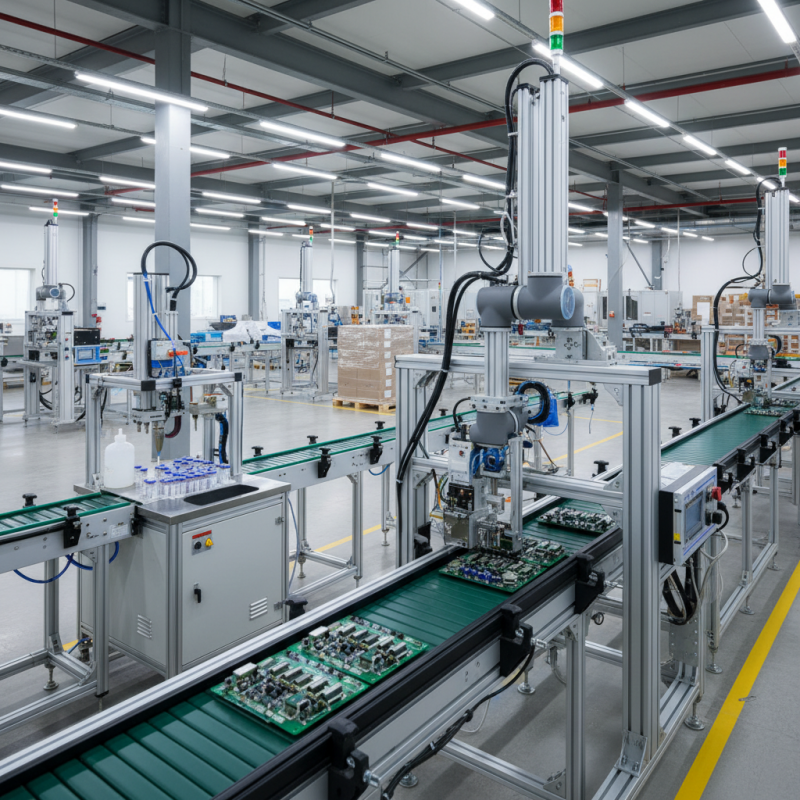

Types of Cartesian Robots in Automation Technology
Cartesian robots are essential in automation technology. They are known for their simple structure and precise movements. Typically, these robots move along three axes: X, Y, and Z. This design allows them to perform tasks such as assembly, packaging, and material handling efficiently.
When choosing a Cartesian robot, consider the payload capacity. Each application has specific needs. Some require light handling, while others need heavy lifting. It's crucial to assess the requirements clearly. A mismatched robot can lead to inefficiencies or failures.
Tips: Always observe the workspace layout. Ensure there’s enough room for the robot's movement. Space constraints can hinder performance. Testing different configurations can reveal the best setup.
Another factor is the operating speed. Some applications demand quick cycles, while others can work slowly. Be sure to test speed adjustments. Balancing speed with precision is often challenging. Finding this balance requires iterative testing and evaluation.
Tips: Keep maintenance schedules in mind. Regular checks can prevent unexpected breakdowns. An unattended robot can degrade quickly. Proper care and monitoring ensure longevity and sustained performance.
Top Types of Cartesian Robots in Automation and Their Applications
This chart illustrates the various applications of different types of Cartesian robots in automation, showcasing their respective application counts. The most common applications are in pick-and-place operations, followed by packaging and assembly tasks.
Key Features of Cartesian Robots
Cartesian robots are pivotal in automation. Their key features make them ideal for various applications. One main feature is their linear motion. This allows precise placement and repetitive tasks. The simplicity in their design means easy programming. Users can quickly adapt them to different functions.
Another notable aspect is their versatility. Cartesian robots can handle diverse tasks. They are great for pick and place jobs. They excel in assembly line operations, too. Users often appreciate how simple it is to integrate them into existing systems.
However, not every setup is perfect. Space constraints might limit their efficiency. Moreover, load capacity varies among different models. Some might struggle with heavier payloads. It's essential to assess specific needs before making a choice. Users should consider their unique environments and tasks. Every application might require a different solution. It's about finding the right balance between capability and practicality.
Common Applications of Cartesian Robots in Industries
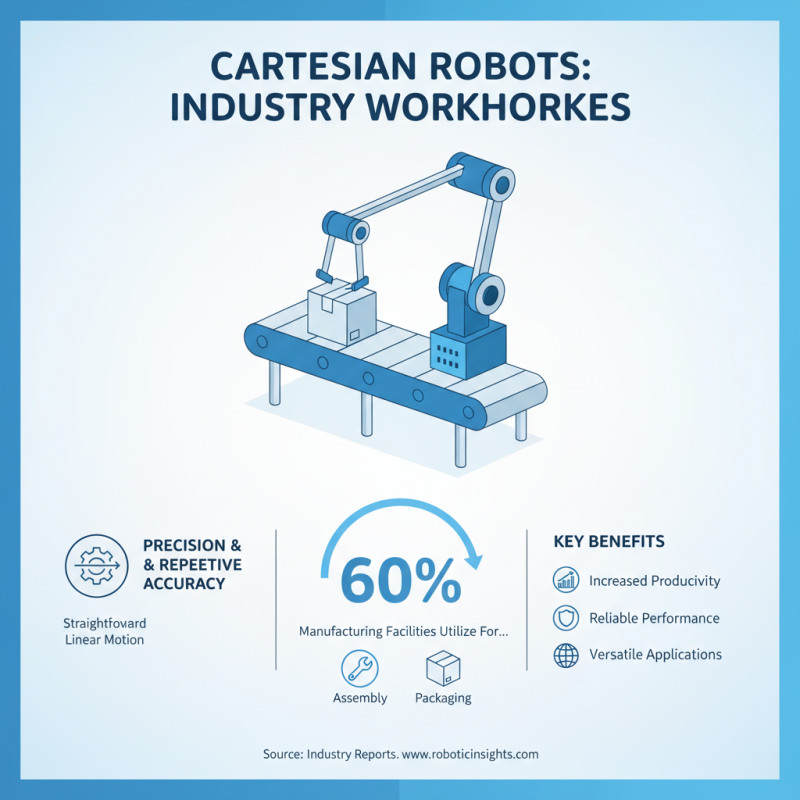
Cartesian robots play a crucial role across various industries. Their straightforward design allows for precise linear movements. This makes them ideal for tasks that require repetitive accuracy. In manufacturing, about 60% of facilities utilize Cartesian robots for assembly and packaging. This indicates their significant value in increasing productivity.
In the automotive sector, Cartesian robots handle tasks like part placement and welding. They can operate with a high degree of precision. Reports show that these robots can enhance throughput by 30%. However, some plants still face challenges integrating these systems smoothly. They require skilled personnel to maintain operational efficiency.
The food and beverage industry also leverages Cartesian robots. They automate processes such as sorting and packing. This sector values robots for their reliability and speed. A recent survey revealed that 45% of food manufacturers have started using automation. Yet, many struggle with scalability in robot systems. This can hinder their ability to meet increased demand.
Advantages of Using Cartesian Robots in Automation Processes
Cartesian robots offer a range of advantages in automation processes. Their simple design allows for easy integration into various systems. With linear movements along three axes, they excel in tasks that require precision and speed. Common applications include assembly, packaging, and material handling. This simplicity leads to reduced maintenance costs and improved reliability.
Another benefit is adaptability. These robots can be programmed for different tasks, making them versatile for changing production needs. Their ability to handle repetitive tasks improves consistency and reduces errors. However, it’s crucial to consider workspace limitations. Some operations may require larger installations, leading to increased space needs.
Despite the many advantages, there are challenges. Programming can be complex for inexperienced operators. Moreover, in environments that demand flexibility, Cartesian robots may be less efficient. Frequent adjustments may disrupt workflow, requiring careful planning. Balancing efficiency with adaptability is essential for effective implementation.
Future Trends in Cartesian Robot Development and Applications
The landscape of Cartesian robots is evolving rapidly. Future trends indicate a focus on greater versatility and improved efficiency. These robots are increasingly finding applications in industries like packaging, assembly, and material handling. They can handle repetitive tasks, which boosts productivity significantly.
As technology advances, integration with AI and machine learning will enhance performance. This combination allows for better adaptability to different production lines. It also helps identify potential faults before they become issues. However, there are challenges. Not all industries may adopt these changes quickly. Many companies may struggle with the initial costs.
**Tips:** When considering automation, evaluate your specific needs carefully. Identify tasks that are repetitive and time-consuming. Investing strategically can yield high returns. Experiment with small-scale implementations before full integration. Engaging with your team during this transition is crucial for success. It can lead to improvements and ideas you might not have considered.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Cartesian Robots in Modern Automation Systems
-
Exploring the Future of Manufacturing: The Rise of Cartesian Robots in Automation
-

Revolutionizing Automation: How Cartesian Robots Shape the Future of Precision Engineering
-

How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Robots for Your Production Needs
-

Why You Should Invest in a Pick and Place Robot for Your Assembly Line Efficiency
-

Why Choose a Pick and Place Robot? Boost Efficiency with 70% Increased Productivity


