How to Use a Robot Arm for Automation in 2026?
As we move into 2026, automation will be more essential than ever. The robot arm stands as a key player in this evolution. It can perform complex tasks efficiently, enhancing productivity in various industries. Factories use robot arms to assemble products with precision. In healthcare, they assist in delicate surgeries. Yet, there are challenges to consider.
Adopting a robot arm isn't without its hurdles. The initial cost can be high. Companies must ensure proper training for their staff. A well-operated robot arm can reduce human error. However, workers may feel threatened, leading to resistance. This highlights a need for transparency and communication.
Moreover, while robot arms are powerful tools, they require constant maintenance. Neglecting this can lead to performance issues. Experimentation with programming is necessary to maximize efficiency. Each industry has unique demands that must be met. Ultimately, a thoughtful approach is needed to fully harness the potential of robot arms in automation.
Understanding the Basics of Robot Arms in Automation
In the ever-evolving world of automation, robot arms are increasingly integral. They perform tasks that require precision and efficiency. Understanding the basics of these robotic systems is crucial for effective deployment in various industries.
Robot arms can range from simple pneumatic systems to complex multi-jointed configurations. Often driven by electric motors, they replicate human arm movement. Learning to program these devices is essential. The process can be daunting for newcomers. Testing and adjusting parameters often lead to unexpected challenges.
Tips: Start with basic projects to get comfortable with the mechanics. Practice programming small tasks. Experimentation enhances your skills. Don't hesitate to iterate on your designs. Mistakes can provide valuable insights.
Additionally, safety must be a priority. Ensure the workspace is free from hazards. Robotics can move quickly; awareness is key. Always assess the setup to avoid accidents. Reflecting on errors or oversights can lead to better practices in the long run.
Key Technologies Driving Robot Arm Functionality in 2026
In 2026, robot arms are evolving rapidly, driven by key technologies. Advanced AI algorithms allow for better decision-making in real time. These systems can learn from their mistakes. This means they adapt to new tasks more efficiently. Machine vision technology enhances their capability to recognize objects. They can detect shapes, sizes, and even colors accurately. This means fewer errors in assembly lines.
Collaboration between humans and robots is crucial. Safety features are now integrated into robot arms. They can halt or slow down if someone gets too close. This makes workplaces safer. However, there is a challenge. Training workers to operate and interact with these robots is essential. Some workers may resist this change, feeling threatened.
Another area is the software behind these machines. Cloud computing plays a role, enabling data sharing among devices. This can lead to improved accuracy over time. However, reliance on internet connectivity poses risks. In case of a network failure, how will robots function? These are important questions as automation continues to grow. The future is promising, but we must address these concerns.
How to Use a Robot Arm for Automation in 2026? - Key Technologies Driving Robot Arm Functionality in 2026
| Technology | Description | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Control | Incorporates machine learning algorithms to enhance precision and adaptability. | Adaptive learning, real-time decision making, improved accuracy. | Manufacturing, assembly, quality assurance. |
| Collaborative Robotics (Cobots) | Robots designed to work alongside humans safely and efficiently. | Safety sensors, ease of programming, user-friendly interfaces. | Assisting in logistics, assembly line support, packaging. |
| Enhanced Grip Technology | Advanced grippers that can handle a variety of shapes and sizes. | Versatility, adjustable grip strength, multi-sensory feedback. | Material handling, food industry, automotive assembly. |
| Cloud Robotics | Utilizes cloud computing for data processing and storage to enhance robot capabilities. | Scalable resources, collective intelligence, remote monitoring. | Smart factories, remote diagnostics, and analytics. |
| Sensor Integration | Integration of advanced sensors for improved awareness and interaction with the environment. | High-resolution vision, force feedback, environmental sensing. | Quality control, precision cutting, assembling tasks. |
Steps to Integrate Robot Arms into Existing Automation Systems
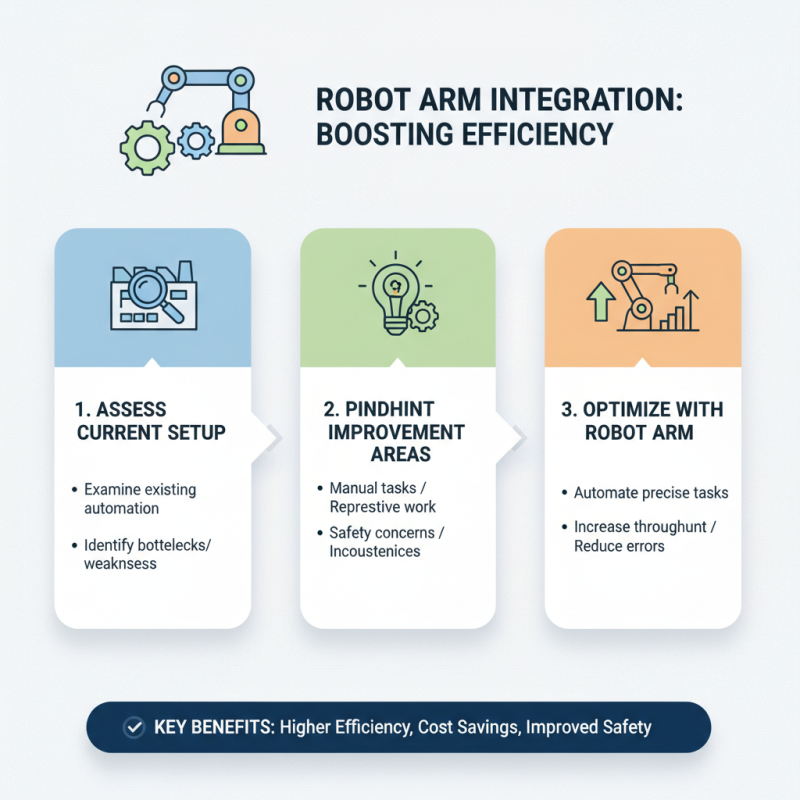
Integrating robot arms into existing automation systems is a vital step for efficiency. Start by assessing your current setup. Identify areas needing improvement. Consider how a robot arm can optimize these processes.
Tips: Evaluate compatibility with current machinery. Train your team on new technology. Communication between equipment is crucial.
Next, focus on programming. Robot arms require specific coding for tasks. Take time to learn the software. It can be complex. Mistakes may happen, so double-check your input.
Tips: Start with simple tasks for the robot arm. Monitor performance closely. Adjust the coding as necessary.
Finally, ensure safety protocols are in place. This includes emergency stops and barriers. An unsafe environment can lead to accidents. Constantly evaluate risks involved with robot operations.
Tips: Conduct regular safety audits. Encourage feedback from operators. Learning from errors improves safety.
Best Practices for Programming and Operating Robot Arms
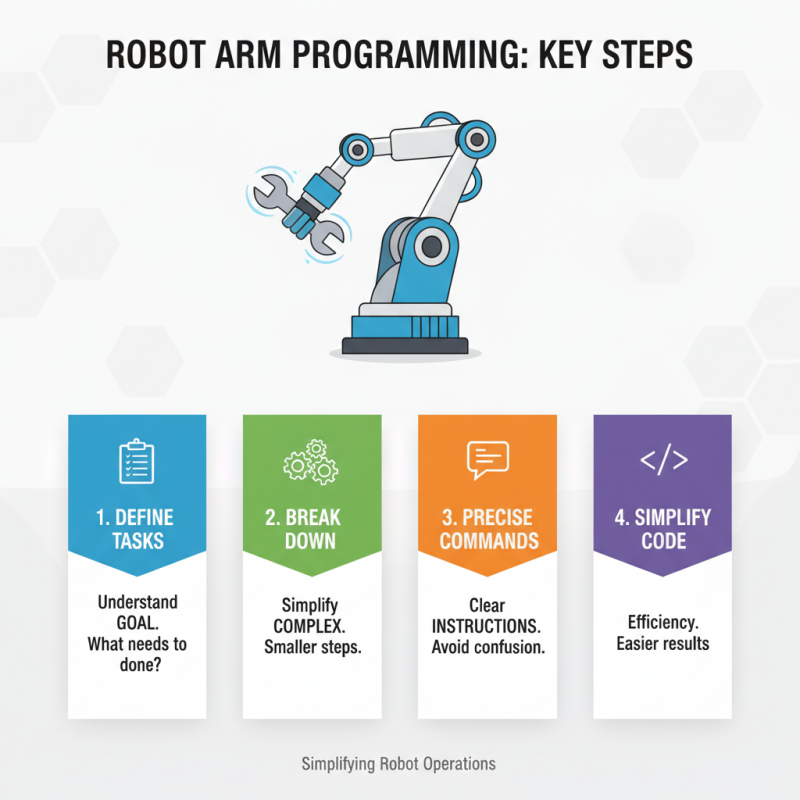
When programming and operating a robot arm, start with a clear understanding of its tasks. Define what you need it to do. Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This can simplify your programming efforts. Use clear and precise commands. The robot arm must understand its tasks without confusion. Avoid overly complex coding; simplicity often yields better results.
Testing is crucial in the programming process. After setting up, run multiple test cycles. Observe how the robot arm performs. Look for any discrepancies in its movements. Keep a record of any errors. Reflect on these mistakes to refine your code. It’s common to face challenges; learning from them is essential. Adjusting your program after each test can lead to improvements.
When operating the robot arm, maintain an awareness of its environment. Pay attention to surrounding objects to prevent collisions. Set safety protocols to protect both the robot and human operators. The workspace should be clear and organized. Regularly update and maintain the robot arm to ensure reliability. Regular checks can help identify potential issues early. Embrace a mindset of continuous improvement for the best results in automation.
Future Trends and Innovations in Robot Arm Automation Technology
In 2026, the landscape of robot arm automation is evolving rapidly.
Advanced sensors will enhance precision.
These sensors allow robotic arms to adapt in real-time. The integration of
artificial intelligence will enable them to learn from their environment.
This learning capability can improve efficiency in production lines and logistics.
However, reliance on AI may create unexpected challenges.
Collaboration between human workers and robotic arms will become increasingly important.
Workers will need to interact with these arms more frequently. For instance,
training workers to understand robotic behavior is essential. This requires a shift in workplace culture.
Some may find it difficult to adapting to this new dynamic. Errors may arise as humans and machines find a balance.
Customization of robotic arms is another trend on the rise.
Companies may tailor arms for specific tasks, increasing versatility.
However, this process poses questions about efficiency versus cost.
Balancing customization with standardized solutions isn't straightforward.
The choice between quick deployment and tailored solutions might not be clear-cut, leading to potential operational challenges.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Industrial Robot Arms in Modern Manufacturing
-

What is Robotic Arm Design and Its Applications?
-

What Are the Top Manufacturing Robots Transforming Industries Today?
-

What is Industrial Robotics and How Does it Transform Manufacturing?
-

How to Efficiently Use XYZ Gantry for Your Next Project Guide
-

Top ASRS Systems to Watch in 2025 for Warehouse Automation Solutions


